Comparison of RS232 and RS485: Both serial communication standards have had a significant impact on industry. Despite being introduced over half a century ago, they are still widely used today. These are two serial communication tools that are not very different from each other. In industry, the difference in application areas is not very significant.
RS232 and RS485 can both be found in applications such as:
- Scientific equipment
- Industrial wireless control systems
- Computers
- Robots
- Medical equipment, etc.
Main Differences
How do we determine which one to choose between RS232 and RS485? Let's examine the main differences:
- Operating Distance
- Immunity to Electrical Noise and Ground Potential
- Number of Transmitters and Receivers
- Data Transmission Speed
| |
RS232 |
RS485 |
| Voltage System |
Based on voltage level |
Differential |
| Single Line Total Driver and Receiver |
1 Driver, 1 Receiver |
32 Drivers, 32 Receivers (Only one driver active at a time) |
| Line Configuration |
Point-to-point |
Multi-drop |
| Max. Operational Distance |
15 meters |
1200 meters |
| Max. Data Transmission Rate |
1MBit/s |
10MBit/s |
| Duplex Mode |
Full Duplex |
Half Duplex or Full Duplex |
| Max. Driver Output Voltage |
+/-25V |
-7V to +12V |
| Receiver Input Resistance |
3 to 7 kΩ |
12 kΩ |
| Receiver Input Voltage Range |
+/- 15V |
-7V to +12V |
| Receiver Sensitivity |
+/- 3V |
±200mV |
Operating Distance
The maximum operating distance between a transmitter and a receiver for RS232 is 15 meters. However, this length can be significantly extended by trading off with slower data rates.
For RS485, the distance is much longer, up to 1200 meters. This is 24 times the distance of RS232. Choosing RS485 would only make sense if the equipment needs to operate far from the transmitter.
Immunity to Electrical Noise and Ground Potential
RS232 operates with a voltage level-based system that performs well when there are minimal differences in ground potential. However, in electrically noisy environments with different potential levels, RS232 is very fragile and allows data corruption.
In contrast, RS485 operates on a differential voltage system. This allows RS485 to exhibit higher levels of noise immunity. The differential voltage system also allows RS485 to provide longer data transmission distances and lower voltage usage, thus helping to increase data speed.
Number of Transmitters and Receivers
An RS232 Serial Interface is meant to connect two devices. There will be one transmitter and one receiver. An RS485 Serial Interface can connect up to 32 devices to a single transmitter.
Also note that RS232 and RS485 are not set in stone. Newer equipment more commonly uses USB interfaces. Therefore, to make different types of equipment or old and new devices work together, conversion from USB to RS232 or RS485; or from RS485 to RS232 and vice versa may be necessary. Converting RS232 to RS485 or vice versa may also be required.
These converters can be easily obtained from our website.
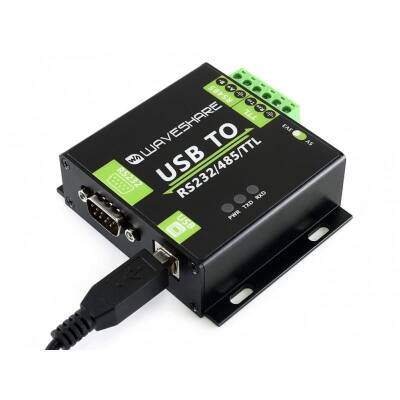

This converter makes a USB port not only to RS485 but also to RS232 and TTL, making it more versatile.
It also has features like galvanic isolation, ADI magnetic isolation, and TVS diode for embedded circuit protection.
Manufactured with an aluminum alloy housing, it is designed to be long-lasting.
Due to its high speed, reliability, security, and versatility, it is unquestionably an ideal choice for industrial equipment use.
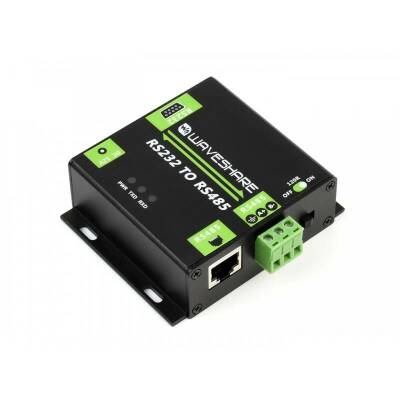

It is an RS232 and RS485 asynchronous bidirectional converter with electromagnetic isolation. It has built-in TVS bidirectional transient suppression diode to protect the device from unstable operations.
Compliant with RS232/RS485 standard, it converts RS232 signal to balanced differential RS485 signal
Stable transmission at speeds from 300 to 115200bps
Built-in power source isolation provides stable isolated voltage, does not require additional power source for isolated terminal
Built-in ADI magnetic isolation provides signal isolation, high reliability, strong anti-interference, low power consumption
Built-in TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) effectively suppresses overvoltage and transient surge voltage in the circuit, lightning-proof and anti-static
Built-in resettable fuse and protection diodes provide current/voltage stable outputs, provide overcurrent/overvoltage protection, enhance shock resistance
Optional RS485 output terminal, enabled/disabled via switch, integrates 120R resistance
Data Transmission Speed
RS232 is more than sufficient for short-distance and low data rate requirements. RS232 has a transmission speed of up to 1Mb/s for up to 15M. However, RS485 has a data transmission speed of up to 10Mb/s for distances of up to 15M. At a maximum of 1200M, RS485 transmits at 100Kb/s.
Real-World Applications
The original purpose of RS232 is to establish a connection between a terminal and a modem. However, over the years, it has been used beyond its original purpose. Most personal computers had RS232-compatible serial ports. It was used to connect peripheral devices such as keyboards, mice, and printers to computers. However, in today's personal computers, USB ports have largely replaced RS232. This is due to the advantages of USB being faster, having lower voltages, and having connectors that are easy to connect and use.
However, RS232 is still used today because it is much more immune to electromagnetic interference. RS232 also has a longer maximum cable length (15 meters for RS232 compared to 5 meters for USB). Many old devices only support RS232 as well. RS232 is also used for laboratory automation measurement. RS232 is used to program PLCs, servo drives, variable frequency drives, and computer numerical control equipment.
RS485 is used in many computer and automation systems. Some examples include robotics, base stations, motor drives, video surveillance, and also household appliances. In computer systems, RS485 is used for data transmission between controllers and disk drives. Commercial aircraft cabins also use RS485 for low-speed data communication. This is because RS485 requires minimal cabling due to its wiring configuration requirements.
However, RS485 is primarily used in programmable logic controllers and factory floors where electrical noise is high. RS485 is used as a physical layer for many standard and proprietary automation protocols to implement control systems, most commonly Modbus and Profibus.
.png)