What is a capacitor? What are its types and what is it used for?

In this blog post, we will answer the question, what is a capacitor? When it comes to electronic circuits, capacitors are undoubtedly among the first circuit elements that come to mind. Let's explore what these small components, also known as capacitors, do and what types exist.
What is a Capacitor
A capacitor is a circuit element that stores electrical energy for a short period. Capacitors utilize the ability of electrons to polarize and store electrical charge within an electric field. This allows them to store electricity. They are constructed with an insulating material placed between two conductive metal plates. The symbol for a capacitor is C, and its unit is the Farad.
When a voltage difference is applied across the terminals of a capacitor, current flows through the circuit. If there is no voltage change across the terminals of the capacitor, it eventually becomes fully charged and stops conducting current. When the voltage across the terminals of the capacitor is changed, current starts flowing through the circuit again. Therefore, capacitor current depends on the voltage change across its terminals.
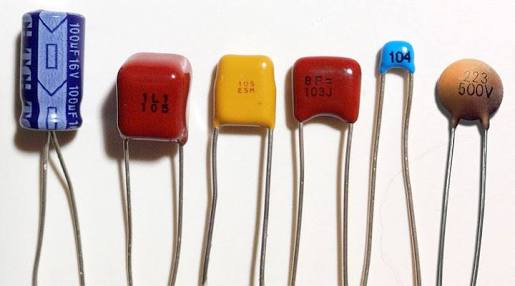
Types of Capacitors
Capacitors are categorized into different types based on specific criteria, including:
- The type of insulating material used between the plates,
- Operating and breakdown voltages,
- The amount of charge they can store. According to these criteria, capacitors are divided into polarized and non-polarized types and into different varieties based on voltage or Farad values.
As mentioned above, capacitors are produced with an insulating material placed between two conductors. Types of capacitors based on the type of insulating material are:
- Ceramic Capacitor
- Electrolytic Capacitor
- Super Capacitor
- Tantalum Capacitor
- Mica Capacitor
- Trimmer Capacitor.
Electrolytic and tantalum capacitors are polarized, while ceramic capacitors are generally non-polarized. Polarized capacitors work only with DC voltage, while non-polarized capacitors can be used with both AC and DC.
Capacity Unit
Capacitors store electrical load as an electric field within the insulating material. Capacity (C) is defined as the ability of a capacitor to store load and is measured in Farads (in memory of Michael Faraday). In the International MKS unit system, 1 Farad is equal to the capacitor's capacity to store 1 Coulomb when a voltage of 1V is applied across its terminals, which is equivalent to 6.275x10^28 electrons. The mathematical expression is as follows:
Blog Latest Additions

Differences Between Li-ion and Li-Po Batteries: Which Battery is Suitable for Which Project?
12.12.2025

MPU-9250: 9-Axis Acceleration Sensor - A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide
28.10.2025

What is ULN2003 ?
13.10.2025
What are Serial Converter Cards (RS232, RS485, TTL)
16.09.2025

What is Peltier and What is its Working Principle?
30.08.2025

Arduino UNO vs Nano vs Mega – Which Should I Choose?
23.07.2025
.png)