What is a Ferrite Core?
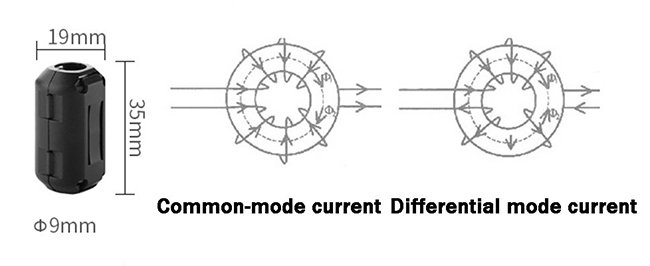
A ferrite core is a type of core made from magnetic material. Its primary component is iron oxide (Fe₂O₃) mixed with other metal oxides. This material is known not only for its magnetic properties but also for its high electrical resistance. It minimizes losses caused by electric currents, thereby improving energy efficiency.

Properties of Ferrite Cores
High Permeability
Ferrite cores easily transmit magnetic flux, making them ideal for electromagnetic applications.Low Hysteresis Loss
Due to their narrow magnetic loop, ferrite materials exhibit minimal energy loss.High Electrical Resistance
This feature reduces the formation of eddy currents (Foucault currents) in high-frequency circuits.
Applications of Ferrite Cores
Power Supplies
Ferrite cores are commonly used in high-frequency transformers, minimizing energy loss while ensuring high efficiency.Filter Circuits
Ferrite cores act as electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters. These filters stabilize circuits by removing unwanted frequencies.Inductors
Inductors utilize ferrite cores to store energy and generate magnetic fields. For example, they are widely used in AC-DC converters.Antennas
In radio frequency circuits, ferrite cores enhance signal reception in antennas.
Advantages of Ferrite Cores
- Deliver high performance in a compact size.
- Provide protection from electromagnetic interference.
- Lightweight and cost-effective.
Things to Consider When Selecting a Ferrite Core
Frequency Range
Choose a ferrite material that matches the frequency range of the circuit.Size and Shape
Selecting the correct size and geometry suitable for the application is essential.Temperature Resistance
Ensure the core can withstand the temperature conditions of its operating environment.
Conclusion
Ferrite cores are critical components that enhance the performance of electronic devices. They are used in a wide range of applications, from power supplies to communication devices, reducing energy losses and providing protection against electromagnetic interference. Selecting the right ferrite core significantly impacts the efficiency and durability of a circuit.
Explore all ferrite core types by clicking here.

The Code of Numbers on Drone Propellers: How to Read Propeller Measurements?

Building a Portable Charging Station with Solar Panels

Differences Between Li-ion and Li-Po Batteries: Which Battery is Suitable for Which Project?

MPU-9250: 9-Axis Acceleration Sensor - A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide

What is ULN2003 ?
.png)